Data centers: opportunities in the AI infra buildout
From semiconductors, industrials, utilities, real estate
The explosive growth of AI is fueling one of the biggest infrastructure build outs we've seen in decades and at the heart of it all are data centers. From semiconductors and industrials to utilities and real estate, a wide range of sectors are lining up to benefit.
Today, we’re kicking things off with a deep look into why we’re entering a Golden Age of AI, how the rapid rise of AI infrastructure is driving an electricity boom, and how the entire AI ecosystem is forming around it. We'll walk through the full AI data center value chain — from sand to smart robots — highlight key players across every vertical, and even start asking the bigger question: what’s the endgame for AI?
And this is just the start. Over the next weeks and months, we’ll continue publishing detailed breakdowns and stock deep dives into the companies best positioned for this generational trend. Make sure to sign up to both of us, so you don’t miss anything.
Overview
Today, we’ll talk about the following:
What’s AI and Why Are We Entering a Golden Age of AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a field of computer science focused on developing systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intellect, such as language comprehension, image analysis, problem-solving, and decision-making. Recent breakthroughs in computing power, specialized hardware, and algorithms—combined with vast data resources—have accelerated AI’s capabilities and adoption worldwide.
AI is now recognized as a transformative force for innovation and productivity across all industries. We are entering a Golden Age of AI, with Brad Smith, Microsoft’s Vice Chairman, likening AI’s impact to that of electricity in previous eras. The surge in AI use is fueled by major investments in data centers and infrastructure, as well as the rapid rise of generative AI platforms like ChatGPT, which reached 100 million users within two months of launch and is now utilized by a significant portion of both US adults and Fortune 500 companies.
AI adoption is outpacing previous technologies, with both businesses and individuals embracing its potential at record speed. The rapid evolution of foundational AI models over the past year and a half signals that, over the next decade, AI will drive major efficiency gains and reshape the global economy and daily life.
The Rapid Rise of AI Infrastructure
AI infrastructure spending is surging to record highs, led by tech giants such as Alphabet, Meta, Microsoft, and Amazon. These companies are rapidly scaling up capital expenditures to expand their networks of AI-ready data centers and computing capacity, primarily to support generative AI, large language models, and cloud services. In 2024, their combined investments were projected at $230–240 billion, a sharp rise from $148 billion in 2023. This upward trajectory is expected to continue, with total capex from these firms likely surpassing $300 billion in 2025.
A major focus is on building advanced data centers equipped with high-performance GPUs—such as Nvidia’s Blackwell chips—and developing custom silicon and energy infrastructure to handle the immense computational demands of AI workloads. Microsoft, for example, plans to invest about $80 billion in fiscal 2025 alone to expand its global network of AI-enabled data centers, with more than half of this spending concentrated in the United States. Meta is also ramping up, targeting $60–65 billion in AI-related capital expenditures for 2025.
This infrastructure boom is not limited to the US; Chinese tech giants and the government are similarly investing heavily in AI parks and supercomputing centers, aiming for global leadership in AI by 2030 (but will not be covered in this article). Meanwhile, the scale and pace of these investments are reshaping the competitive landscape, driving innovation in both hardware and energy solutions for data centers, and establishing AI infrastructure as a critical foundation for future economic growth and productivity.
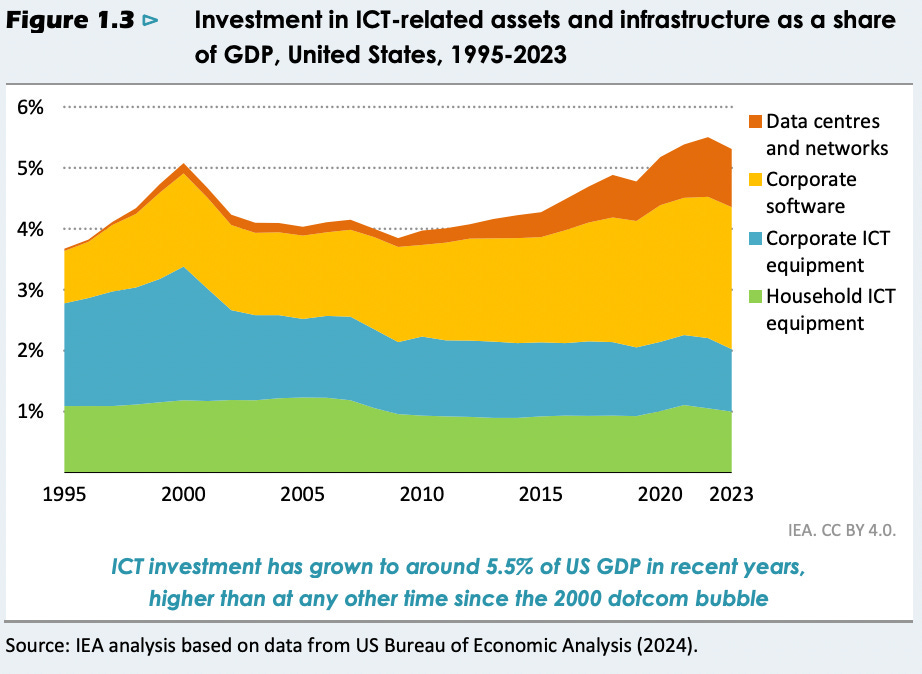
Investment in ICT-Related Assets and Infrastructure
ICT investment in the U.S. has reached approximately 5.5% of GDP in recent years, the highest level since the 2000 dotcom bubble. This growth is driven primarily by increased spending on corporate software and data centers, alongside steady investments in corporate and household ICT equipment. The trend highlights the rising importance of digital infrastructure in the modern economy.
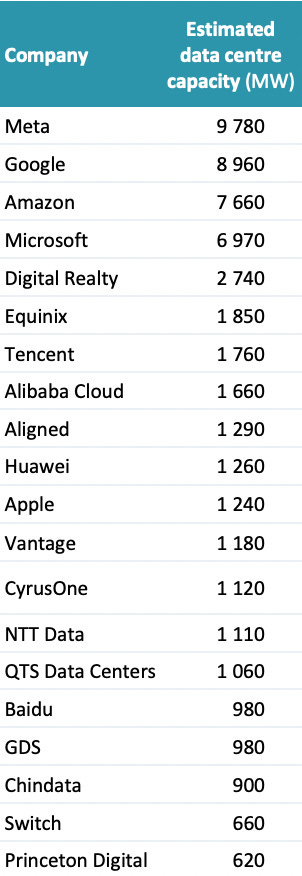
Data Center Capacity
Meta, Google, and Amazon lead the world in data center capacity, each surpassing 7,000 MW. Meta tops the list with an estimated 9,780 MW, followed by Google (8,960 MW) and Amazon (7,660 MW). Microsoft and Digital Realty round out the top five. The data highlights the dominance of U.S. tech giants in global digital infrastructure, with significant contributions also from Chinese and global colocation providers like Tencent, Alibaba Cloud, and Equinix.
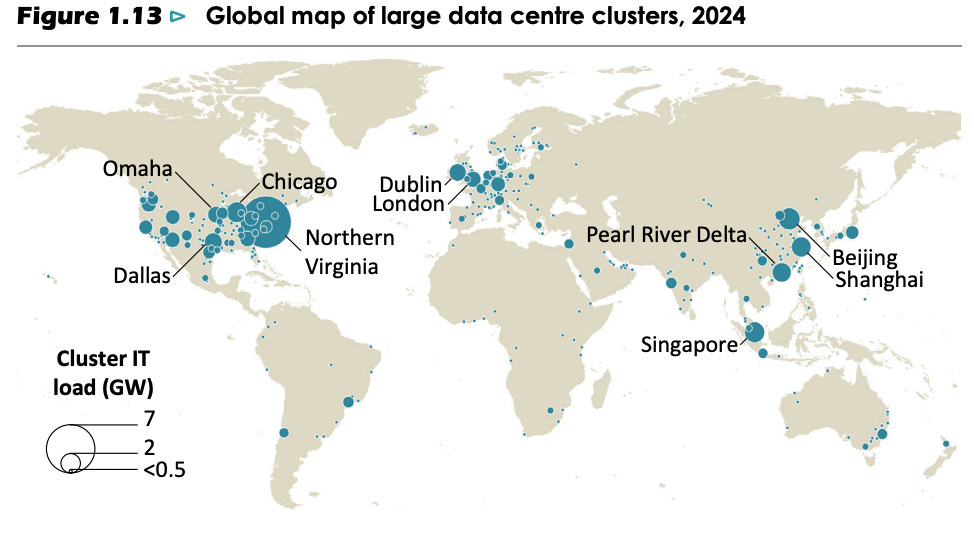
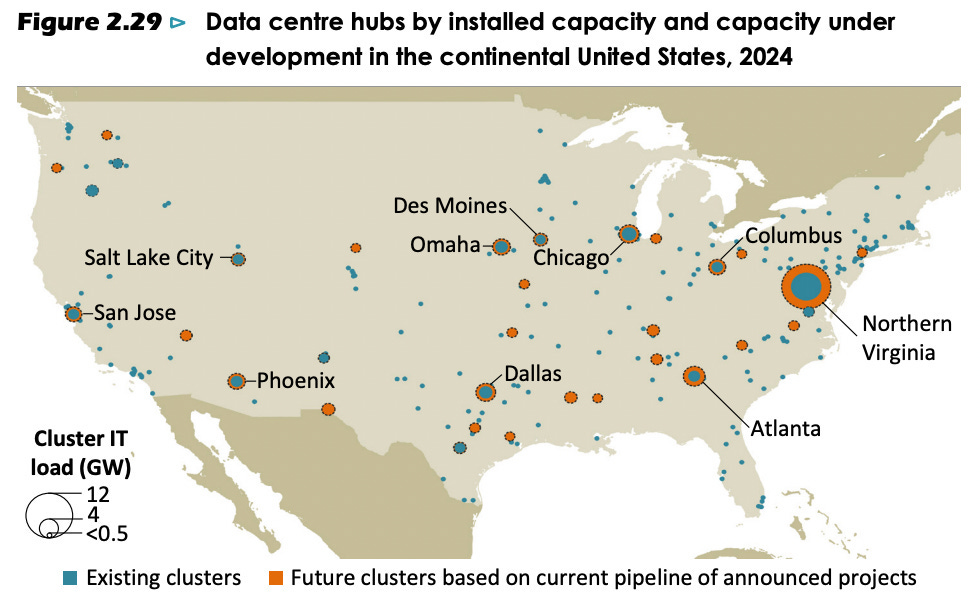
Data Centers Worldwide
AI is driving a surge in data center construction worldwide. Currently, about 8,000 data centers are in operation globally, with 33% located in the US, 16% in Europe, and 10% in China. The number of new projects is rapidly increasing to support AI development and deployment.
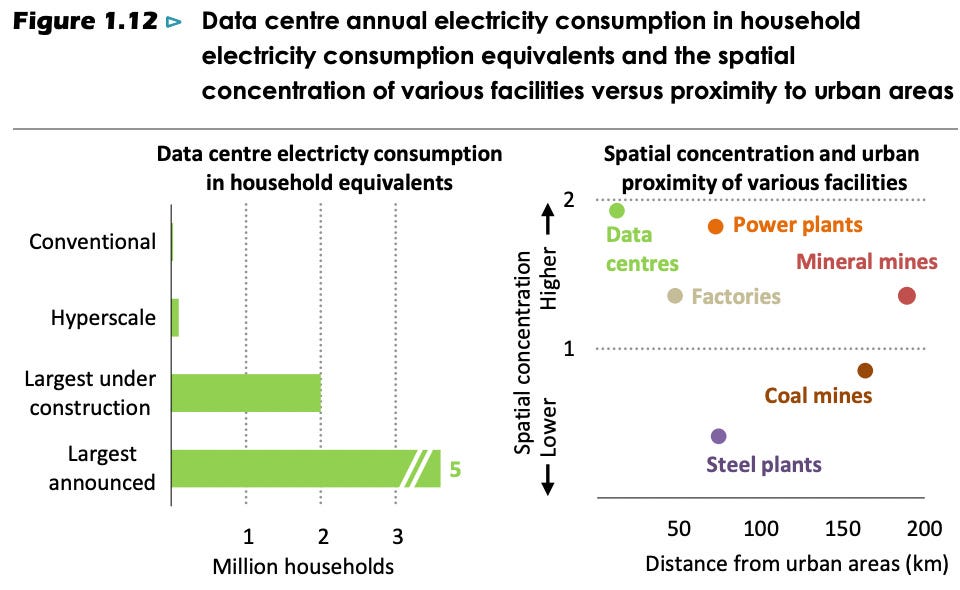
The Electricity Boom
Data centers have historically only modestly grown as a share of global electricity consumption rising only from 1% in 2005 to 1.5% in 2024, despite explosive growth in digital activity and internet usage, largely due to advances in energy efficiency. However, with most gains from consolidating enterprise data centers already realized, AI servers already highly optimized, and physical limits to further chip miniaturization approaching, future efficiency improvements are becoming more challenging.
As AI adoption accelerates, energy use by data centers is now set to surge. In 2024, data centers consumed about 415 TWh, or 1.5% of global electricity, but this is projected to more than double to roughly 945 TWh by 2030, driven mainly by generative AI, which will account for 41% of total data center demand by then, up from 16% today. While this will mean data centers make up about 3% of global power use by 2030, their contribution to total electricity demand growth will remain under 10%, less than sectors like industrial motors, air conditioning, or electric vehicles.
The impact will be uneven: in advanced economies, data centers are expected to drive over 20% of electricity demand growth to 2030, and in the US, their share of national electricity use could climb from 4% today to as much as 9% within a decade. In Ireland, data centers already account for 21% of electricity consumption. This concentration will put significant pressure on local grids, with the risk that up to 20% of planned data center projects could be delayed due to grid connection bottlenecks and infrastructure constraints.
So, while data centers’ global energy footprint will remain a relatively modest slice of total demand, the rapid expansion of AI is making their growth a key driver of electricity demand in many regions, raising new challenges for grid management, energy infrastructure, and generation and therefore opportunities for many companies providing solutions to those sectors.
The AI Ecosystem
A handful of leading companies, with Nvidia being the most important, dominate the rapidly growing AI ecosystem’s infrastructure layer. This segment provides the specialized hardware and scalable cloud platforms essential for managing and processing the massive datasets required to train AI models and deliver real-time inference.
AI computing relies on specialized chips built for the heavy processing demands of both training and inference. Nvidia leads this segment with its Hopper and Blackwell GPUs, while AMD and major tech firms are developing their own AI hardware. TSMC is the primary foundry, and platforms like Nvidia’s CUDA offer essential software tools and libraries for AI development.
Cloud providers and data center operators—including AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Equinix, and CoreWeave—supply the storage, networking, and GPU resources required for large-scale AI workloads. These facilities depend on advanced hardware, efficient networking, sophisticated cooling, and robust power infrastructure to manage the high computational and energy demands. Power management systems, backup solutions, and advanced cooling technologies are critical for stable and efficient operations.
At the application layer, foundational models like OpenAI’s GPT underpin generative AI services such as ChatGPT, which are widely adopted and can be fine-tuned for diverse use cases. The rapid evolution and deployment of these models are driving broader AI integration across industries and consumer products.
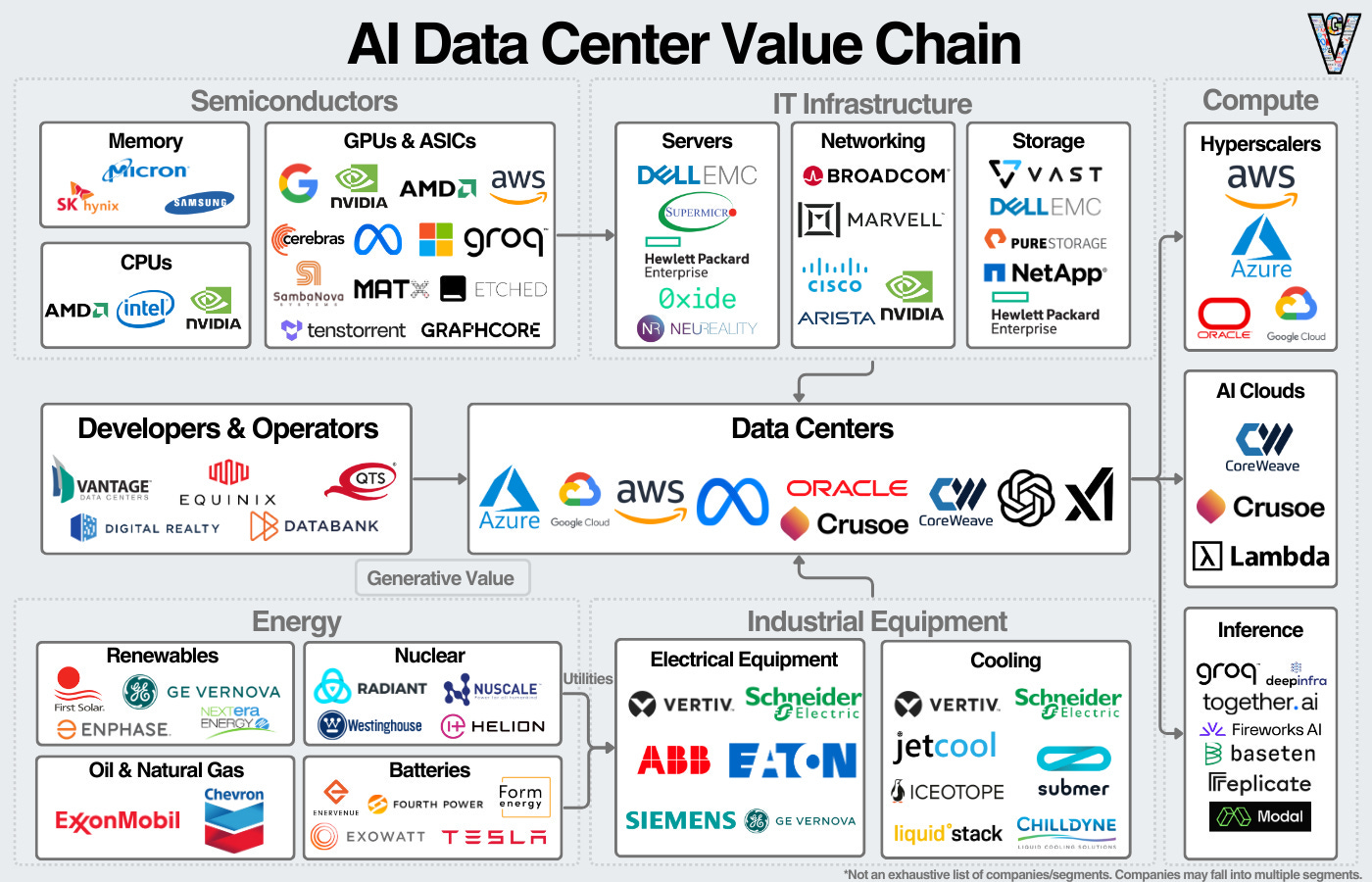
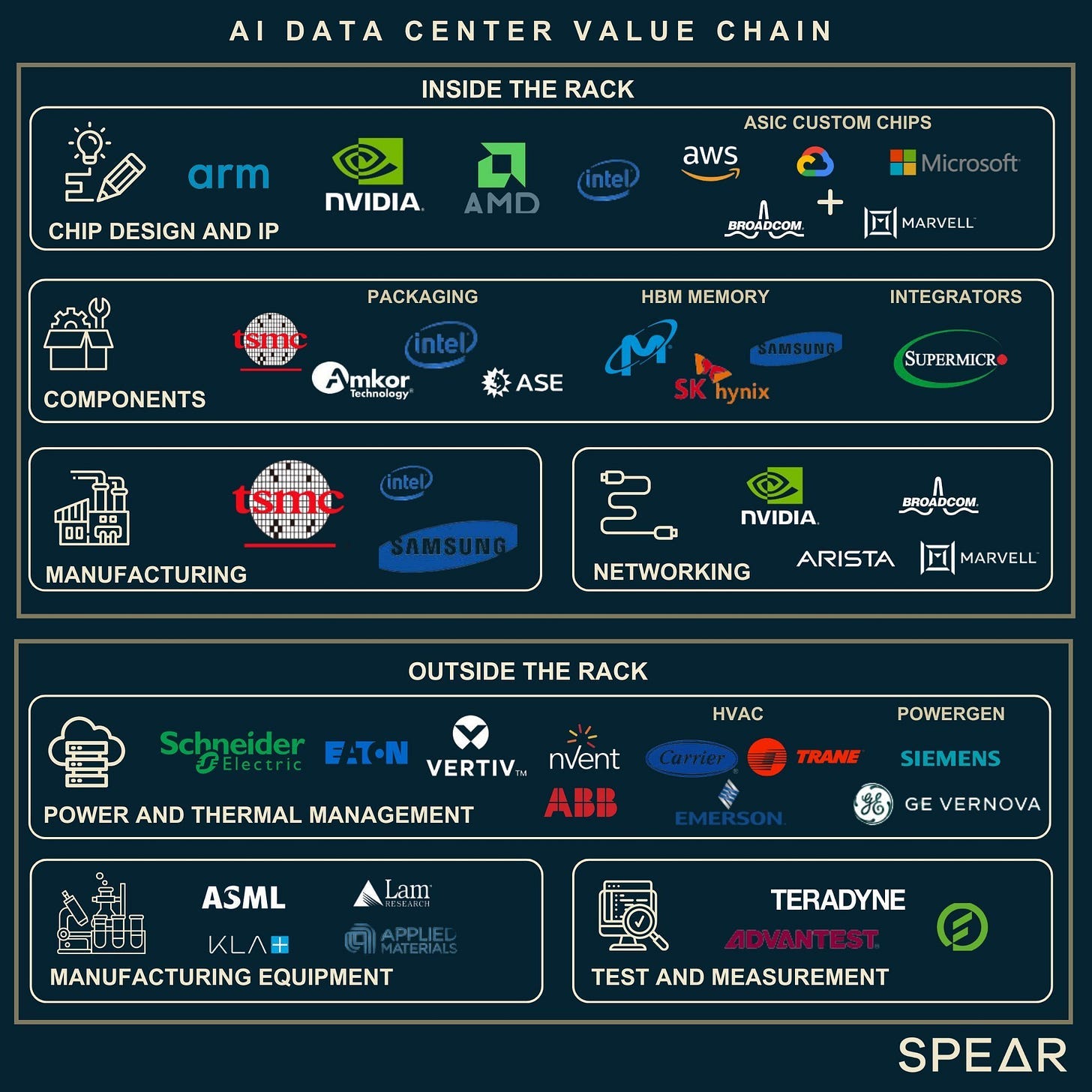
The AI Data Center Value Chain
As you can imagine, building and operating the infrastructure that powers AI models is no small feat, it’s a highly complex and resource-intensive process.
At the heart of it all lies the data center rack, picture a refrigerator packed with high-performance electronic components. This is where the real magic happens: AI models are trained and deployed on specialized chips that crunch massive amounts of data every second.
But what surrounds these racks is just as important. Supporting AI data centers requires an entire ecosystem of specialized hardware, high-speed networking equipment, advanced cooling systems, and a resilient energy infrastructure to handle the immense computational demands.
This means major investments in everything from power generation and transmission to distribution and backup systems. Effective power management is critical, not just to deliver electricity to individual chips, but also to ensure constant uptime and system stability.
To keep temperatures under control, data centers deploy cutting-edge cooling technologies from traditional air conditioning units to advanced liquid cooling systems designed to manage the intense heat generated by modern AI hardware.
From generating the electricity, to moving it efficiently, to managing heat and ensuring continuous uptime, every component must work in harmony to keep AI running at full throttle.
From Sand to Smart Robots: How AI Infrastructure Comes to Life
Step 1: It all starts with sand
Crazy as it sounds, the AI that's writing your emails or driving your car starts with sand, not just any sand, but high-purity quartz. This ultra-clean material is refined down to nearly perfect silicon, the basic ingredient in all computer chips. Without it, there’s no tech, no smartphones, no ChatGPT, no Tesla. Nothing.
Key companies:
Unimin (owned by Covia) – one of the largest producers of high-purity quartz.
Sibelco – global supplier of industrial minerals.
Step 2: Turning sand into silicon wafers
That purified silicon gets melted down and shaped into smooth, flat discs called wafers. Think of them like the pizza dough of the chip world, everything gets built on top of them. These wafers are super thin and incredibly delicate. Even the tiniest speck of dust can ruin an entire batch. That’s why chip factories look more like sci-fi labs than traditional manufacturing plants.
Key companies:
SUMCO (Japan)
GlobalWafers (Taiwan)
Shin-Etsu Chemical
Siltronic (Germany)
Step 3: Drawing Tiny Circuits with Light
Next comes the lithography step. Here, advanced machines use light to “draw” billions of tiny circuits onto those silicon wafers. It’s kind of like using a stencil and a flashlight to design microscopic highways where electrical signals will travel. This step is so precise it literally happens at the atomic level and the machines used can cost over $100 million each. No joke.
Key companies:
ASML
Applied Materials
Lam Research
Tokyo Electron
Step 4: Building the Brains – GPUs
Once all the circuits are in place, the wafers are cut up into individual chips. These chips go into GPUs, which are basically the brains behind AI. Originally built for video games, GPUs can handle massive amounts of data at once, making them perfect for teaching AI to learn from huge datasets. Companies like NVIDIA and AMD are the rockstars of this space.
Key companies:
NVIDIA
AMD
Intel
TSMC
Samsung
Step 5: Enter the Data Centers
Now those GPUs are installed into huge data centers, giant buildings filled wall-to-wall with servers. They look like something out of a spy movie, with blinking lights, heavy cooling systems, and a constant hum of power. These centers are where AI models live, train, and run 24/7. But powering them is no small feat, they need a ton of electricity and specialized cooling to keep everything from melting down.
Key companies:
Amazon (AWS)
Microsoft (Azure)
Google (Cloud)
Meta
Digital Realty, Equinix – data center REITs
Alibaba Cloud, Tencent Cloud (China)
Switch, CyrusOne, QTS Data Centers
Step 6: Training the AI
Inside these data centers, AI gets trained kind of like a really intense workout for a robot brain. The models are fed massive amounts of data and taught to find patterns, make decisions, or generate content. Training a large model can take weeks or even months and requires some serious computing firepower. This is the phase where the AI “learns” how to do things like chat, paint, or even diagnose illnesses.
Key companies:
OpenAI (ChatGPT)
Anthropic (Claude)
Google DeepMind
Meta (LLaMA)
Amazon (Titan)
Hugging Face - open-source model library
Microsoft
Step 7: Bringing AI to Life – The Applications
Once the AI is trained, it can be used in all sorts of ways:
Generative AI: Tools like ChatGPT, image generators, and AI music creators.
Predictive AI: Systems that forecast weather, predict stock trends, or manage supply chains.
Computer Vision: Tech that lets machines “see”—like facial recognition or self-driving cars.
Physical AI: Think robots, drones, automated warehouse arms—AI that moves and interacts with the real world.
Key Players in Each Vertical
The Data Center Racks
Semiconductors:
EDA/IP: Cadence, Synopsys, ARM.
Semiconductor equipment manufacturers: ASML, AMAT, Besi etc.
Memory: SK Hynix, Micron, Samsung.
GPUs and AI data center racks: Nvidia.
Manufacturing AI chips (Foundries + assembly): TSMC, Amkor, ASE.
Networking: Arista Networks, Credo, Broadcom, Marvell.
Data Center Rack Assembly (EMS): Supermicro, Flex, Jabil, Celestica.
The Data Center
Hyperscalers:
The Tier 1s: Amazon, Meta, Alphabet, Microsoft, Oracle, Alibaba.
The up and coming: CoreWeave, Nebius.
Buildings:
REITs: Equinix, Digital Realty.
Engineering and equipment rentals: United Rentals, Jacobs Solutions etc
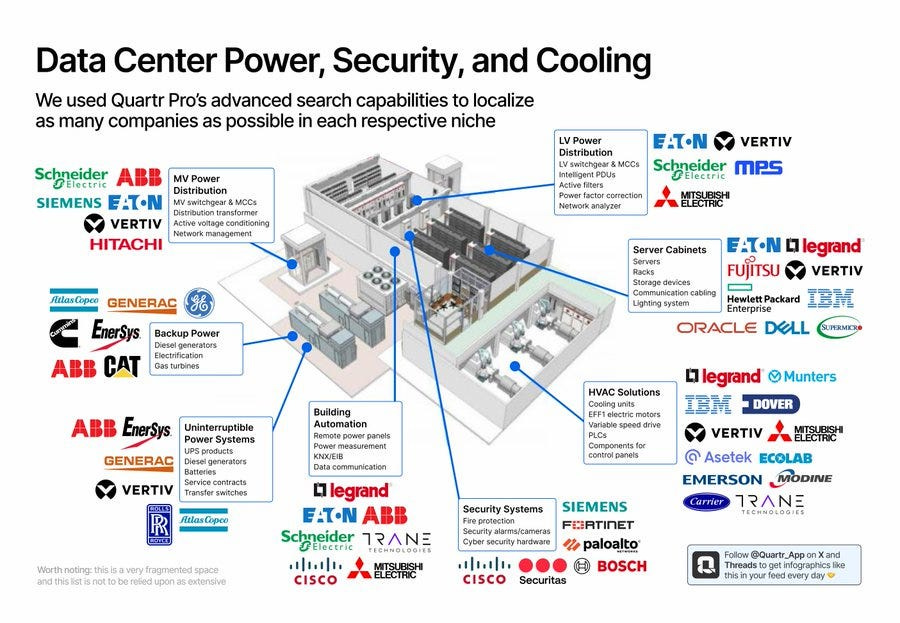
Data Center Power:
Cooling Solutions:
HVAC: Trane Technologies, Johnson Controls, SPX Technologies, Carrier, Alfa Laval.
Liquid cooling: Vertiv, Munters.
Power Generation and Networks:
Utilities: Constellation Energy, Vistra, AES Corp, Nextera Energy.
Networks: Quanta Services, Itron, Hubbell.
Energy generation: First Solar, Siemens Energy, GE Vernova
What is The End Game of AI?
There are many applications of AI and we are just getting started! Let’s look at the types of AI:
Generative AI:
Think of ChatGPT and all the new products and services that have emerged using AI’s capacity to “think” and “reason” based on your prompt. This includes everything from text generation, image and video creation, to music composition and code writing. It’s reshaping industries like marketing, entertainment, software development, and education.Predictive AI:
Used in finance, healthcare, and logistics, predictive AI identifies patterns in data to forecast future outcomes. It powers stock price predictions, disease diagnosis, customer behavior forecasting, fraud detection, and supply chain optimization. Its strength lies in turning vast datasets into actionable insights with minimal human intervention.Physical AI:
This includes robotics and autonomous systems, machines that can interact with and navigate the physical world. Think self-driving cars, warehouse robots, AI-powered drones, and even humanoid robots. These systems combine sensors, real-time decision-making, and machine learning to operate independently, transforming sectors like transportation, manufacturing, agriculture, and defense.
The convergence of these AI branches generative, predictive, and physical—points toward a future where AI becomes a seamless extension of human capability. Whether it’s personalized education, autonomous infrastructure, or human-AI collaboration at scale, the ultimate goal may be an intelligent ecosystem where machines anticipate needs, make decisions, and take actions to improve quality of life, productivity, and even creativity.
But with that potential comes responsibility: ensuring ethical use, data privacy, bias mitigation, and maintaining human oversight are all critical parts of this journey.
And for that reason, it’s difficult to say whether there’s actually gonna be an End Game with AI. The only thing we know for sure, is that AI will probably be able to do a lot more in a decades time.
Final Thoughts
We are living through one of the most profound technological revolutions in history, fueled by the explosive rise of artificial intelligence. What started as isolated breakthroughs has now erupted into a full-blown arms race, with the largest, most powerful, and best-capitalized companies the world has ever seen pouring hundreds of billions into AI infrastructure. This battle isn’t just about who has the best models, it's about raw computing power, energy, data, and the physical infrastructure behind it all.
The investments being made today into AI data centers, semiconductors, networking equipment, energy infrastructure, and specialized real estate are creating a once-in-a-generation opportunity. We are entering a Golden Age for companies that sit anywhere in the AI value chain — from chipmakers to utilities to industrial giants — and this boom is only just beginning.
Now that you understand the macro story and the sheer magnitude of this trend, it's time to dig deeper. The real winners will be the companies that build and power this new world. We’ve already started publishing deep dives into some of the top beneficiaries of the AI boom and there’s a lot more coming over the next weeks and months.
If you want to stay ahead, make sure to subscribe to us so you don’t miss a thing!
Make sure to share it as well, so we can reach more people!
Here are some of our previous deep dives and stocks we are bullish on:
ASML: The most innovative company in the world will 2.5x its EPS by 2030
AMD: The next data center conglomerate
Flex: The electronics manufacturing giant building Nvidia’s servers and enabling reshoring is becoming a better business
Synopsys: The best chip designing company out there
Itron: Riding the grid investment super cycle and enabling smart grids
Halma: High quality compounder in safety, health and environmental technologies
Quanta Services: Countercyclical compounder riding a multi decade infrastructure buildout
Infineon: Power semiconductor leader with strong structural drivers (AI power and China auto) amidst a cyclical recovery
Disclaimer: The information provided on this Substack is for general informational and educational purposes only, and should not be construed as investment advice. Nothing produced here should be considered a recommendation to buy or sell any particular security.















AI & Data Center drive Cloud Shared Responsibility and Cybersecurity Solution and Service Boommm.